Logging Oxygen Sensors Using OBDLink
This entry was posted on April 28, 2016.
Oxygen sensors play a key role in engine performance and keeping emissions under control. Their purpose is to measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust, providing your vehicle's computer with information whether the air/fuel mixture is burning rich (less oxygen) or lean (more oxygen). If an oxygen sensor goes bad, it can damage the catalytic converter (a very expensive fix!), reduce fuel efficiency, and substantially increase the amount of harmful pollutants in the exhaust.
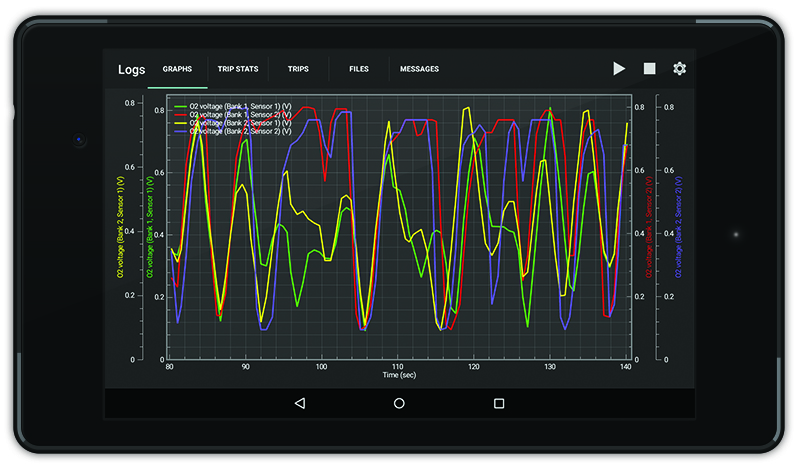
Using OBDLink's logging feature, you can graph the transitions of each oxygen sensors’ voltage (usually there are 2 sensors but some vehicles have up to 4), and know when one becomes faulty.
A good oxygen sensor should produce an oscillating waveform at idle, making voltage transitions from near minimum (0.1v) to near maximum (0.9v) within 100 milliseconds. Always consult the manufacturer service information before making any repairs.
- If the sensor BEFORE the catalytic converter graphs a straight line, there may be a problem with that sensor
- If the sensor AFTER the catalytic converter graphs a straight line, you could have a bad converter
Follow these steps using the OBDLink app:
- Tap the 'Logs' icon from the Home screen
- Tap 'Menu' in the top right
- Set 'Graph Item 1' to 'O2 voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)'* - this is the oxygen sensor BEFORE the catalytic converter and the upstream flow
- Set 'Graph Item 2' to 'O2 voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)'* - this is the oxygen sensor AFTER the catalytic converter and the downstream flow
- Repeat steps 2 & 3 if you have 3 or 4 oxygen sensors in your vehicle
*Terminology may be different for some vehicle's depending on year, make, and model.